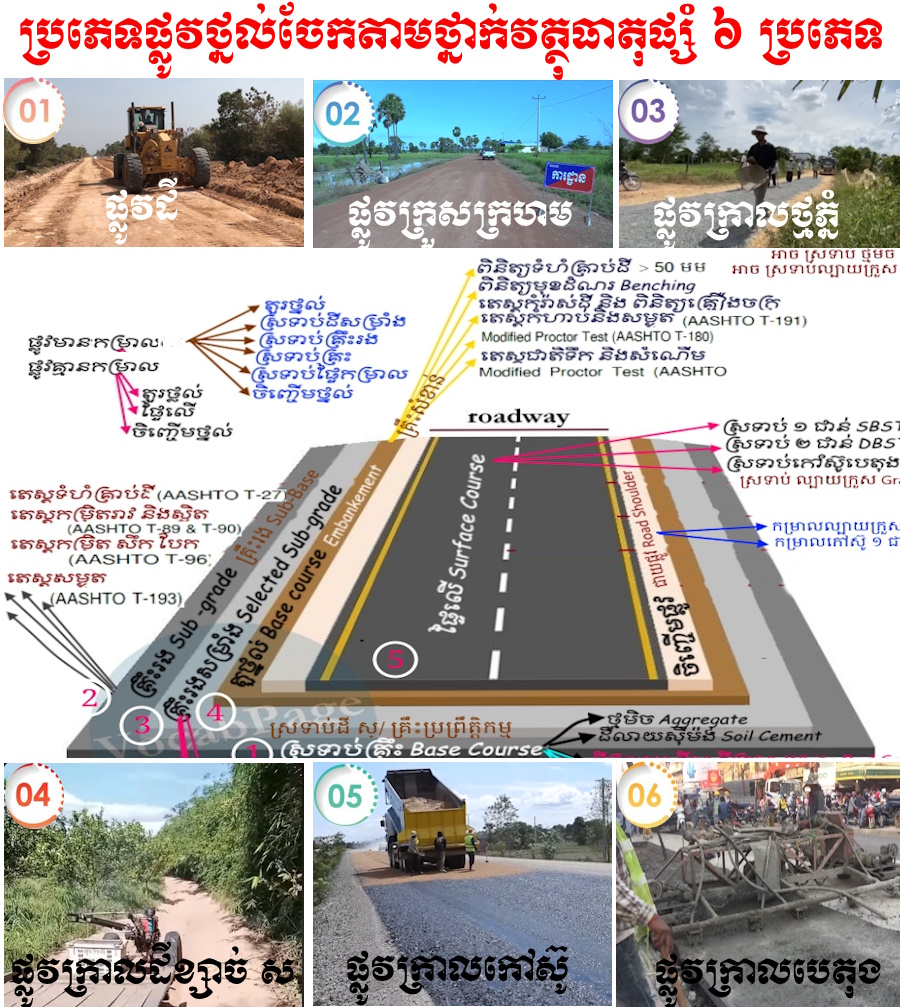
ប្រភេទផ្លូវថ្នល់
រូបភាព
- EARTHEN ROADS: ផ្លូវដី These are earthern roads in which earth is the primary constituent of road probably provided within the village area.
- WATER BOUND MACADAM ROADS (W.B.M.): ផ្លូវក្រួសក្រហម It consists of broken pieces of stones of dimension varying from 25 mm to 75 mm which are laid in three layers on prepared sub-grade. The larger sized pieces of stones are laid within the backside course. This kind of road can also be usually provided within the village area, nowadays W.B.M. is the compact base for the bituminous road and concrete road.
- MURRUM ROADS ផ្លូវថ្មភ្នំ/ ក្រួសភ្នំ : Murum is a obtaine by meteorological agencies from disintegration of igneous rocks, these roads are known as murrum roads.
- EARTHEN ROADS: Earthen materials is an impure type of limestone, this roads are provided where lime is offered in an affordable quantity. The earthen roads are in low high quality and efficiency.
- BITUMINOUS ROAD OR TAR ROADS ផ្លូវកៅស៊ូ : It is the structure of flexible pavement water-bound macadam surface is prepared then smaller chips of stones, size varying from 16 mm to 20 mm with bitumen are laid, in the thickness varying from 30 mm to 40 mm. Bitumen acts as a binder, this type of road gives a smooth wearing to course for the layer at the top of the road. The life span of the bituminous road is short and durability is less as compared to the concrete road. There is a possibility of developing corrugations due to heavy traffic, its repairs work is easy but the maintenance cost is more.
- CEMENT CONCRETE ROAD :ផ្លូវ បេតុង This road is the structure of the rigid pavement. It consists of a rigid wearing surface on the top of the sub-base then with base course and then sub-base to compacted sub grade. The life span of the concrete road is long and its durability is also more as compared to the bituminous road. There is no possibility of developing the corrugations due to rigid pavement, its repair work is difficult due to the rigidity of concrete & its maintenance cost is quite low. The classification based mostly on traffic volume or tonnage has been arbitrarily fixed by completely different agencies and there might not be a common settlement regarding the limits for every C classification group.
- LIGHT TRAFFIC ROADS ផ្លូវចរាចរទាប: The roads that are carrying 400 vehicles each day is known as light traffic roads.
- MEDIUM TRAFFIC ROADS ផ្លូវចរាចរមធ្យម : If a road is carrying 400 to 1000 vehicles per day then it is a medium traffic road.
- HIGH TRAFFIC ROADS ផ្លូវចរាចរខ្ពស់ : If a road is carrying is greater than 1000 vehicles per day, then it is considered as high traffic highway.
- MAJOR DISTRICT ROADS (MDR): ផ្លូវតំបន់ ១ The responsibility of construction and maintenance of those roads lies with district authorities; however, the state government provide a grant for the development of those roads.
- OTHER DISTRICT ROADS (ODR): ផ្លូវតំបន់ ២ This has a decrease in design specification than MDR.
- VILLAGE ROADS (VR): ផ្លូវតំបន់ ៣ These roads are essential from the viral area improvement perspective, they are typically unmetalled with single-lane width of stabilized soil or gravel. The responsibility of construction and maintenance of those roads lies with the native district authorities.
- NATIONAL HIGHWAYS (NH): ផ្លូវជាតិ Roads having the width from 7 m to 15 m connect the capital cities of the various states in the country are called as national highways. The national highway makes a very important link or network for transportation of men and materials. National highways carry fast and heavy traffic.
- STATE HIGHWAYS (SH): ផ្លូវខេត្ត The roads having the width varying from 7 m to 10 m connect the national highways and the district places in states and are known as state highways (SH). State highways carry medium to fast traffic.
- DISTRICT ROADS:ផ្លូវស្រុក Roads which connect each district place to the taluka place are known as district roads, the width of this road varies from 5 m to 8 m. The design speed of vehicles on the district roads is less than the design speed on highways, these roads carry moderate traffic.
- PEDESTRIAN WAYS ផ្លូវថ្មើរជើង : Pedestrian ways are solely constructed for pedestrians and no vehicles are permitted in this way.
- CYCLE TRACKS: ផ្លូវកង់ Cycle tracks or bicycle tracks are provided on either side of the pavement for cyclists therefore they will travel safely.
- MOTORWAYS ផ្លូវរថយន្ត/ ផ្លូវម៉ូតូ : Motorways are often known as expressways, just a few vehicles are accessible to make use of this kind of road. The cars which might move with high-speed acceleration are permitted in this way. Motorways make the journey quick and supply comfort for high-speed vehicles.
- EXPRESSWAYS ផ្លូវល្បឿនលឿន : Expressways are a separate class of highways with superior facilities, design standard and through routes having a really excessive quantity of traffic. These highways should allow solely fast-moving vehicles. Expressway could also be owned by the central government or state government relying on whether the route is a national highway or state highway.
- Arterial roads: ផ្លូវភ្លោះធំ The streets primarily for through traffic on a steady route, however with an excessive level of traffic mobility are generally known as arterial roads.
- Sub-arterial roads:ផ្លូវភ្លោះរង Roads mainly through traffic on a stationary route, however have a lower level of traffic mobility than arteries, commonly known as sub-arterial roads.
- Collector streets ភ្ជាប់ផ្លូវភ្លោះ : The Street which provides access to arterial streets, collect and distribute traffic from local streets is known as collector streets.
Local streets: The Street which provides access to abutting streets are known as local streets.
- FLEXIBLE ROADS ផ្លូវកម្រាលទន់ : Flexible roads include a versatile layer as a pavement surface, which requires proper maintenance, otherwise it may be disintegrated simply with heavy traffic. All types of roads are under this category apart from concrete roads.
- RIGID ROADS: ផ្លូវកម្រាលរឹង Rigid pavements are non-flexible and cement concrete roads in this category.
- PLAIN AREA ROAD: ផ្លុវវាលរាប The roads constructed on the flat flooring are known as plain area roads.
- HILL AREA ROADS: ផ្លូវខ្ពង់រាប Roads constructed in hilly areas are known as hilly space roads or ghat roads. Typically, these are provided on the hill in a spiral form.
ការកសាងស្រទាប់នីមួយនៃគ្រឹះផ្លូវថ្នល់ អាចមាន ពី ៤ ទៅ ៦ ស្រទាប់ អាចជា
- ផ្ទៃលើ់ Surface
- ស្រទាប់រឹង Base
- ស្រទាប់ ទម្រ Sub-base
- ស្រទាប់គ្រឹះ Sub Grade
- ស្រទាប់ទន់ Flexible ដែល ស្ថាបនាអំពី Asphalt, Gravel, Laterite, Grass ad Salt
- ស្រទាប់រឹងមាំ Rigid ដែលស្ថាបនាអំពី បេតុង ដុំថ្ម ដុំឥដ្ឋ
















































Please Fedback my New article
ReplyDeleteSpread footing is used to deliver and transmit the load coming from the structure to the ground.
A floating slab is a reinforcement concrete slab used for a shallow foundation. The floating slab is a type of concrete slab. This type of slab is placed on the ground without any anchoring.
Termite shields are of three kinds, physical termite shield, Chemical termite shield, and roof and wall termite resistant frame.
blurb
ReplyDeleteunsplash
houzz
indiegogo
teliportme
Education should never be a privilege only for the wealthy. Every student deserves a fair chance at success. That’s why programs like Free college tuition for low-income students are so important—they open doors for those who need it most. Let’s support equal opportunities in education!
ReplyDelete